Saturday, December 8, 2007
ICAITS017C Maintaining System Integrity
This course is part of the System Maintenance Group (ITSM):
• ICAITU007B Maintain equipment and consumables
• ICAITS015B Install software applications
• ICAITS017C Maintain system integrity.
Nominal hours: 20
System Maintenance aims to provide you with technical skills to uphold an organisation's aims and services with respect to dealing with people and processes in the information technology industry.
This group of courses assumes that you have access to a computer and the Internet and that you have previous knowledge and experience using the Internet and Windows Explorer software.
Performance criteria
1. Carry out file maintenance
o File back-ups are carried out.
o Back-ups are determined and stored according to organisational guidelines.
o Records of back-up are maintained.
2. Carry out virus scanning
o Virus protection is maintained.
o Detected viruses are reported to supervisor and are removed.
3. Follow software copyright procedures
o Software licenses are monitored.
o Illegal software is determined.
o Illegal software is reported to supervisor.
4. Record software licenses
o Licensed software is determined.
o Records of license number and location are maintained.
o Personal computers and networks are checked for illegal software.
o Illegal software is reported to supervisor.
5. Restore system backup
o Back-ups are restored.
o Restore procedure are determined according to the organisational guidelines.
o Restore is carried out under supervisor instruction.
o Restore carried out is recorded according to the organisational guidelines.
[top of page]
Resources needed
Standard platform
• Standard computer requirements for all IT programs
Computer requirements
To study any IT program you will require:
Computer
PC capable of running Microsoft Office. Pentium III or later is preferred.
Printer
Any A4 printer
Operating system
Windows 2000 or later version. Windows XP is preferred.
Office suite
Microsoft Office Professional 2000 or later version. MS Office 2003 Professional is preferred. (if MS Office software is only used for educational purposes, it is available at special pricing from the student computer shops of most universities. Proof of student status is required.)
Internet connection
Any dial-up or broadband account with email and newsgroup access. Broadband is preferred, especially at Certificate 4 level, where some large software files are downloaded.
The computer requirements listed above apply to all IT programs. However, particular courses sometimes have additional requirements. Refer to programs for information on courses.
OLI-supplied resources
• ITSM Learning guide
• ITSM Introduction and Assessment Book
Required text
Not applicable
Special software
Not applicable
Observer
It is the student's responsibility to locate a suitable person to act as an observer for certain assessment tasks.
[top of page]
Learning topics
The following list of topics appears in the contents page of the course learning materials:
• Legal and ethical obligations
• The Information Age
• When are practices legal and ethical?
• When are practices legal and ethical?
• Legal and ethical obligations
• Software programs
• Installing software applications
• Installing software in Windows
• Installing WinZip
• Installing a .zip file
• Installing Microsoft Office 97/2000
• Uninstalling a program
• Backup and restore
• Why backup?
• Backing-up files
• Restoring files
• Using backup in Windows
• Using Restore in Windows
• Viruses
• What is a virus?
• Symptoms of viral infection
• Sources of viral infections
• Using anti-virus software
• Hardware faults
• Coping with hardware faults
• Recognition of hardware faults
• Administration of hardware faults
• Cleaning and maintenance procedures
• Preventive maintenance
• Maintenance schedule
• Cleaning specific components
[top of page]
Assessment outline
Competency Test 1
• backup and restore data
• software viruses - indicators, detection, reporting and removal
• software licensing and copyright
• observer tasks - virus checking and backup and restore C: drive
[top of page]
FAQs
What sorts of things can affect system integrity?
A primary cause of disruption to system integrity are computer viruses. But apart from malicious damage, accidents and hardware failure can also disrupt system integrity.
What does backup mean? I already keep more than one copy of my important documents?
Backup can be achieved in many ways. It is important to understand the more business oriented backup using a backup utility such as Microsoft Backup, rather than just copying individual files. "Proper" backup utilities can automate backup in various ways and can make backup easier and safer.
ICAITS015B Install software applications
Install software applications
Outline of unit content
On successful completion of this competency, learners should be able to record, prioritise and escalate client requests. Specifically, the learner should be able to:
1. Determine software or software upgrade requirements of clients:
o Document and report client requirements to supervisor.
o Act on supervisors instructions to meet client requirements in line with organisational guidelines, corporate purchasing, licensing arrangements and budget.
2. Obtain software or software upgrade:
o Obtain software under instruction from management.
o Determine and record licensing requirements in line with organisational guidelines.
3. Install software or upgrade:
o Install upgrade to meet supervisor’s instructions.
o Undertake process so clients experience minimal disruption.
o Computer is installed to accept software.
o Testing and acceptance are carried out in line with corporate guidelines.
o Client requirements are satisfied. Amendments are made as required for client, or client is referred to appropriate person/supervisor if necessary.
Resources
Web resources
SiSoftware Sandra (the System ANalyser, Diagnostic and Reporting Assistant) is an information & diagnostic utility. It should provide most of the information (including undocumented) you need to know about your hardware, software and other devices whether hardware or software.
www.sisoftware.demon.co.uk/sandra/
Recommended reading
Installing software
Andy Ashdown and Andrew Easton
ISBN: 0 7894 7291 0
Publish date: May, 2001
72 pages
Dorling Kindersley (Essential Computer Series)
Description
Installing Software helps you master the basic skills of adding and removing programs on your PC, and includes: performing complete and custom installs from a CD-ROM, installing internet downloads, using a decompression program, downloading and installing a font, upgrading using Windows Update, using patches to fix problems, installing plug-ins, acquiring driver software, and maximizing your hard disk space by uninstalling old programs.
Glossary
Sandy Bay Software's PC Webopaedia
An excellent on-line PC encyclopaedia, containing detailed descriptions of many PC terms and links to other pages. www.pcwebopaedia.com/
Free On-line Dictionary of Computing
The most comprehensive dictionary of its kind, containing over 11,000 definitions. UK link - can be slow at times. foldoc.doc.ic.ac.uk/foldoc/index.html
Activities
Activity 1: completing a system specification
Before you install software or even before you purchase it, you need to know if your existing hardware has the capacity and capability of running the new software. Now think what this means if you are required to organise a major upgrade of software organisation-wide. You need to know details of all of the computers on which the software/upgrade will be installed. You need to know if the PCs have enough memory, hard disk space, if the version of the operating system is compatible, are the workstations connected to the network?
If your organisation consists of a number of sites, it would take a lot of your time, if every time you needed to do an install, you needed to visit each site and carry out an investigation.
Information Technology departments usually keep detailed records of all the computer systems in the organisation. More often than not this information is stored in a database and is updated every time a change is made to a computer. The record containing the computer system details is often referred to as a System Specification.
Completing your system specification You will be provided with a blank system specification form. You are required to complete all the details on the System Specification form for the workstation you are using.
Aside from the tools provided within Windows, there is a range of software tools on the market that can assist you in gathering the information required.
Click here to download your System Specification form
Remember you will need to update your System Specification each time you install or uninstall software. Why? Because the amount of used/free hard disk space will have changed!
Activity 2: software maintenance log
It is important to maintain a record of the software maintenance carried out on a computer. There are a number of reasons for this:
• Assists in maintaining software licence control
• Assists in troubleshooting software problems
• Provides a “software history” for the computer
In this activity you are required to design a Software Maintenance Log. The purpose of the log is to record all software installations, upgrades, un-installs and major configuration changes for the workstation you are using.
Design a software maintenance log
Design a form to record the installation and modification of software installed on your system. This form should include fields for the following information:
• Details of the system to which log refers
• Location of system
• Details of installation (name of package, version, and any other details eg uninstall, reinstall, new install, upgrade, configuration change)
• Name of Support Person undertaking the work
• Date of installation/modification
You may use the following example as a guide:
Software Maintenance Log
PC Make/Model Location
PC Serial No.
Date Software Package and Version Type of Maintenance* Name Signature
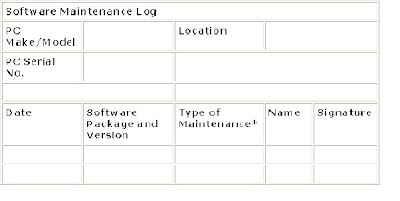
* Might be a New Install, Upgrade, Configuration Change, Un-install, or Re-install
You are to record on this form all software installations/modifications/ uninstalls carried out.
Activity 3: software installation checklist
Having satisfied yourself that the available hardware has the capacity and capability to handle the software that you are going to install, and having purchased the software and recorded the licensing arrangements, you now need to plan the actual software installation, configuration and testing.
At all times it is important to try to minimise disruption to the client. You should follow organisational guidelines in relation to this. However, at the very least, you should contact the client, organise a time suitable for the install, and advise the client as to the length of time it is likely to take.
There are quite a number of tasks associated with software installation. These can be broken into three categories:
• Pre-installation planning
o Call logged to Help Desk
o System specification checked
o Software licence checked
o Software obtained and backed up
o Installation and configuration requirements obtained
o Installation scheduled with client
• Pre-installation system preparation and application testing
o Virus scan run
o User data backed up
o Critical system files backed up
o Startup disk available
o Temp and Internet Temp files deleted
o Recycle bin emptied
o Scandisk run
o Disk Defragmenter run
o Selection of existing applications tested and output produced
• Software installation, configuration and testing
o Software installed in accordance with organisational standard
o Software configured according to requirements
o Software tested & output produced
• Post-installation application testing and documentation
o Existing applications re-tested and output produced
o System specification updated
o Software licence recorded
o Software maintenance log updated
o Help Desk call closed
o Follow-up call to user
o Client acceptance/sign-off
As you can see, there are a lot of tasks to keep track of. To assist in this process and ensure that all of the tasks are completed, a Software Installation Checklist form is often used. The Checklist lists all of the tasks to be undertaken and, as they are carried out, they are ‘checked off’ the list. The Checklist is used every time a software package is installed.
Based on the list of tasks discussed above create your own Software Installation Checklist form. Make sure you include space to record the package being installed, details of the system on which it is to be installed and columns so that you can ‘check off’ each task as you complete it.
Review questions
Questions:
1. What is a software licence?
2. What does EULA stand for and what is it?
3. What are the differences between a single-user, multi-user and site licence for software?
4. List 5 effects of using illegal software.
5. When installing software on a client’s workstation, it is important to be aware of the client’s needs. List 6 behaviours that you should exhibit when interacting with the client.
6. Pre-Installation System Preparation and Application Testing are important aspects of the software installation process. List 9 tasks that should be undertaken as part of this process.
7. Why would you run disk defragmenter before installing a software application?
8. You have installed an upgraded version of a software package on a client’s workstation but the package will not work. Will you:\
(a) Advise the client there is a problem and make a time to come back and fix it.
(b) Advise the client there is a problem, re-instate the original software from the backup and advise client of the action you intend to take.
(c) Ask the client to locate another machine to use in the interim and take away the machine with the faulty software to fix it.
(d) Stay and fix the problem no matter how long it will take.
9. Before installing a new application, a software support person should advise the client to:
(a) backup all programs.
(b) backup all data files.
(c) compress the hard disk.
(d) printout a directory tree structure of the workstation.
10. What does the term ‘preferred supplier’ mean?
Answers
1. A software license allows the purchaser to use the software under certain specified conditions. The license also stipulates what the purchaser may or may not do with the software.
2. End User Licence Agreement. The EULA specifies the conditions under which a purchaser may use the software.
3. Single-User: Software may be loaded on only one machine at a time.
Multi-User: Specified number of licenses (eg 5-user; 10-user licence). May be loaded on a maximum of machines allowed by licence.
Site: Licence that allows loading of the software on any/all machines at one physical location.
4. Increased chance of viruses
No support from manufacturer
No access to upgrades
No manuals
Prospect of prosecution and fines
5. Be diplomatic and polite
Make sure you don’t “talk down” to the client
Always ask before using the client’s telephone
Don’t pile your belongings or tools on top of the client’s things
Make sure you accommodate the client’s urgent business
Protect the confidentiality of the client’s data
6. Scan for viruses
Back up user data
Back up critical system files
Make sure a Startup disk is available
Delete Temp and Internet Temp files
Empty the Recycle bin
Run Scandisk
Run Defragmenter
Test a selection of existing applications and produce output
7. So that the application is installed into a contiguous block of space on the hard disk.
8. (b) Advise the client there is a problem, re-instate the original software from the backup and advise client of the action you intend to take.
9. (b) backup all data files
10. A preferred supplier is one who has a special relationship with a customer/company. This relationship usually means that the customer will, other things being equal, give the supplier a certain amount of (almost guaranteed) business during the course of a year. In return, the supplier is expected to match certain standards of quality and timeliness.
The NSW HSC Online© site is bound by the responsibilities outlined in the disclaimer.
Monday, December 3, 2007
ICAITU007B Maintain equipment and consumables
Maintain equipment and consumables
On completion of this unit, learners should be competent in keeping computer systems operational.
They should have the ability to:
1. Decide on an appropriate course of maintenance to ensure devices continue to work reliably.
2. Use appropriate methods to manage consumables.
3. Provide appropriate support to isolate and rectify common faults in peripheral devices.
Preventative Maintenance
Learn about the importance of preventative maintenance Exercise 1
Short answer and true or false questions Exercise 2
Multiple Choice questions
Case study 1
Client Services Environment case study and a written task for you to complete Exercise 3
Short Answer Questions Practical Exercise Hardware Maintenance
Practical exercises for you to complete to learn about hardware.
Sample Project
Mario & Luigi's Internet Café. Set up your own internet Café Glossary
Explanation of terms that will help you with this unit Other Resources
Useful links
Preventative Maintenance
It is important to maintain equipment and consumables. Routine or preventative maintenance ensures that the computer equipment will remain in good working order. Examples of preventative maintenance on computer equipment is the cleaning of your keyboard, monitor and mouse.
The keyboard can be cleaned by turning the keyboard upside down and gently tapping the bottom of the keyboard. Monitors can be cleaned with a damp cloth. The mouse requires regular maintenance as the tracking ball under the mouse collects dust as it rolls inside the mouse. To clean the mouse, turn it upside, remove the panel, clean the tracking ball and the rollers inside the mouse.
Printers require routine maintenance as well. Clearing out paper jams, changing cartridges and cleaning the printer will lengthen the life of your printer. Most printers have a print head cleaning function or you can use a print head cleaning kit. Make sure that you read the manufacturer's instructions before you perform any maintenance.
Consumables like floppy disks, CD's and paper require correct storage to ensure that they will be usable when required. They should be stored in a clean, dry area. To ensure that the moisture content of the paper is kept at an optimum level, paper should be stored in a sealed container. Moist paper tends to curl and jam in the paper path of a printer.
Glossary
Backup A method of storing files for use in an emergency. The backup medium includes tape, disk or CD
Defrag Defragmentation is the process of locating the non contiguous fragments of data into which a computer file may be divided as it is stored on a hard disk , and rearranging the fragments and restoring them into fewer fragments or into the whole file.
Hard Copy The output from software applications printed and stored on paper.
Inventory A record of items in stock. This is used to track consumables or to accurately describe devices.
Maintenance Maintenance refers to rectifying faults and changing settings or components to ensure that equipment continues to work effectively.
Non-routine Maintenance When a device or its components are serviced to rectify a specific fault. Procedures such as replacing a faulty floppy disk drive or adding extra RAM to a poorly performing computer are some examples of non-routine maintenance.
Print Server A network node which stores print jobs and then passes them to the printer. This action frees up the network from the slow printer output speed causing network congestion.
Printer Bubble Jet A printer which uses the process of spraying the ink onto the page by superheating a bubble of ink to eject the spray onto the paper.
Printer Dot Matrix An impact printer that uses a series of pins to press an inked ribbon onto the paper surface to create a character or image.
Printer Driver The software the printer uses to interpret the signals from the various applications that have the ability to output hard copy.
Printer Impact A printer that forms the characters and images on the paper by physical contact. They can be used to make a real time carbon copy.
Printer Ink Jet A non-impact printer that sprays the ink onto the paper through a series of fine nozzles.
Printer Laser A printer that uses electrically charged powdered toner to create the image, which is then fused onto the paper using heated rollers. They are more expensive to purchase than ink jet printers, however they are often economical to operate.
Printer Networked A printer that can be set up as a network node and store and then print jobs from a number of remotely connected computers.
Printer non-impact A printer that does not cause an impression to be made on the page.
Purchase Order The initial order which is a record of the items to be ordered and the associated auditing details.
Routine Maintenance When a device or its components are serviced as a matter of course. Procedures such as adding paper to the printer tray, cleaning the ink jet cartridges, aligning the print heads or changing toner cartridges are some examples of routine maintenance.
ScanDisk Scandisk is a Windows utility used to check your hard disk for errors and to correct problems that are found.
Other resources
John Hamilton (editor), 2000, Fundamentals of Systems Administration, Eastern House, Victoria
John Hamilton, Chris Huber, Ian Kenny, 2001, Essentials of IT Volume 2, Eastern House, Victoria
The GoVET website has current resources available for teachers and students.
You can find definitions and quizzes on this site.
The Be Box Zone has a number of interesting bits of information as well as a diagram of a motherboard.
Loring Prest's Web site has a schematic of an older style computer motherboard.
Activities
Exercise 1
1. What does maintenance mean?
2. Ink jet printers are more economical than laser printers.
TRUE FALSE
3. Describe the process of replacing a printer cartridge in an ink jet printer that uses a colour cartridge and a black cartridge.
4. Printer driver means: -
The person using the printer The software that the printer uses The interface card used by the printer
5. Paper supplies should be stored in a sealed container.
TRUE FALSE
6. After installing a new word processing application on a client's computer the printer will not print. You suspect the printer driver has a fault. What would you do?
7. Paper dust is abrasive to the mechanism of a printer. What should you do to ensure the printer does not suffer undue wear?
8. Your printer is printing with bands across the characters. What is the likely cause of this and what could you do to remedy the fault?
9. Modern laser printers are only able to print in black.
TRUE FALSE
10. Describe the OH & S issues associated with servicing printers.
Suggested answers
Suggested answers
Exercise 1
1. Maintenance refers to rectifying faults and changing settings or components to ensure that equipment continues to work effectively.
2. False. The initial cost of a laser printer is higher as is the cost of a toner cartridge, however the speed of printing and the number of pages able to be printed before the cartridge must be replaced is much higher in a laser printer.
3. Your answer should include the following steps.
• move carriage to servicing position
• remove cartridges
• replace cartridges
• align cartridges
• test print
• record in the maintenance log
4. The software that the printer uses.
5. True. To ensure that the moisture content of the paper is kept at an optimum level, paper should be stored in a sealed container. Moist paper tends to curl and jam in the paper path of a printer.
6. Your answer could include the following procedures.
• run a test print, if available, from the printer program.
• download the latest printer driver if available from the web site of the printer manufacturer.
• delete the current printer driver.
• install the new printer driver.
• print a test page.
• load the new application and try a test print from that program.
7. Your answer could include the following procedures.
• use higher quality paper
• regularly vacuum dust from the mechanism.
• keep the printer covered when not in use to exclude other types of dust from the mechanism.
8. The likely cause is the print head requires cleaning. Your answer could include the following:
• use the print head cleaning function (this uses a lot of ink).
• use a print head cleaning kit.
9. False. There are colour laser printers on the market. They are still more expensive to purchase and maintain than black and white printers of a similar quality.
10. Your answer could include the following procedures.
• avoid contact with the skin of either ink or toner powder by using gloves.
• avoid inhaling the fumes or the powdered toner by using a dust mask and also service in a well-ventilated room.
• avoid inhaling the paper dust when cleaning the paper path.
Exercise 2
Multiple choice
1. A backup procedure is:
A. a method of going back to a previous copy
B. a method of storing files for use in an emergency
C. a method of compressing files ready for archiving
D. a method of saving a hard copy of all text documents
2. DPI stands for:
A. desirable Print Index
B. dots Per Inch
C. double Page Indexing
D. dots Per Interval
3. Most printers currently use:
A. parallel communication
B. serial communication
C. wireless communication
D. network communication
4. Which of the following is most likely to ensure a properly functioning mouse?
A. updating the mouse drivers
B. cleaning the buttons
C. cleaning the ball and rollers
D. cleaning the mouse pad
5. A keyboard can be effectively cleaned by:
A. vacuuming the keyboard.
B. removing the key caps and brushing the keyboard.
C. holding the keyboard upside down and gently tapping the bottom.
D. hosing carefully with distilled water.
Suggested answers
Exercise 2
Multiple choice
1. B
2. B
3. A
4. C
5. C
Case Study
Client Services Environment
Most organisations have computing equipment which will require maintenance to keep it in good working order. In some cases individuals are responsible for their own equipment, in other organisations there is a section, often the information technology section, that is responsible for all computing equipment in the organisation.
To ensure that resources required at a critical time are available and in good condition, it is often necessary for the information technology section to manage the ordering and storage of consumables like printer cartridges, storage devices and cables. It is also their responsibility to monitor the shelf life of these consumables. This includes rotating stock to make sure that the consumables that are purchased first are used first.
Your task
Choose an information technology organisation that you have studied or participated in for work placement and complete the following questions
OR
Use the following scenario to answer the questions.
Scenario
Helpdesk Solutions is an organisation that receives and logs up to 400 helpdesk calls a day. The organisation prides itself on its prompt call logging service and problem resolution rate.
Equipment maintenance is a key factor in reducing these help desk calls. Common routine procedures are documented on the intranet as are frequently asked client questions with appropriate answers.
The helpdesk software that is used by this organisation is called Remedy. It records all calls, who is responsible for resolving each call and the progress of each call. Have a look at the Remedy internet site to find out more about this product:
Questions
1. How does the organisation create an effective service environment through verbal and non verbal communication?
2. Each organisation will have procedures to follow when dealing with a client problem.
For example when a hardware problem occurs, such as a faulty keyboard, service personnel will generally follow a different action plan to that used to resolve a software problem, such as word processing software not opening a document.
With respect to this: -
a. what are the organisation's guidelines for client hardware maintenance procedures? How do these differ from the way in which software problems are actioned?
b. make a list of consumables that the organisation will need to order and maintain.
c. how does the organisation maintain a log of all requests for work to be carried out on a particular computer or printer? Create an example for a typical computer fault. The diary/log can be paper-based or electronic.
Sample format -
Date of problem Name of person who logged problem Nature of problem/task Nature of action taken Date action taken Further action required
** Additional details may be required depending on the nature of the organisation. Check if a maintenance log already exists in the organisation.
3. If there are a number of problems with a client, how are the problems prioritized ?
4. What method is there to keep track of client documents and service records to ensure that previous service actions can be reviewed and documents can be reloaded from the backups?
5. Write a report, summarizing the following procedures carried out on a typical networked workstation and printer which are in use over the full working day. Base your answer on your work placement or your school/college computers.
a. routine maintenance (such as cleaning mouse rollers)
b. common maintenance problems (replace printer cartridge)
c. problem solving techniques used (such as file will not open in the application used to create it)
d. suggestions for ongoing reliability of the system (maintenance and performance improvements).
Suggested answers
Case Study 1
Your responses could include the following.
1. Staff meetings, emails, memos, notice board, letters, call logs, intranet.
2. (a)The organisation would have guidelines relating to warranties and contracts for hardware. Hardware problems are usually diagnosed via tests to identify the problem and the faulty hardware is replaced. If necessary the supplier of the product is contacted. Software problems are actioned by giving the user a set of instructions to try to resolve the issue. If a bug is discovered in the software, the details of the bug are logged with the supplier.
(b) Consumables include paper, toner cartridges, floppy disks, zip disks and CD's.
(c) Helpdesk software is used to record all the calls logged. Reports can be produced for specific computers, printers or type of printer
3. Organisations set guidelines for prioritisation and escalation of problems. Those problems which prevent a person from performing their job or a critical task are dealt with first, such as a user being unable to log on, or a faulty monitor preventing a user from completing an urgent task. Upgrades and enhancements are actioned when there is time.
4. The organisation would have a backup policy. Usually corporate data is backed up daily. Individuals often use network drives which are backed up. As helpdesk software records all client calls, a service report would be available detailing the backup file location for the user.
Exercise 3
1. What are some of the problems that a user would experience when a disk has many fragmented files on it?
2. How are fragmented files made contiguous when maintaining computer storage devices?
3. When should a backup of files be done?
4. What are some of the ways in which files can be kept safe from damage ?
5. What is the difference between SCANDISK and DEFRAG when managing files.
6. What is the point of optimising a hard disk drive? Choose the best answer from the options below:
A. making the commonly used files smaller in size.
B. making the commonly used files more secure.
C. making the commonly used files load faster.
D. making the commonly used files save faster.
7. Summarise the common directory structure created on most personal computers.
8. If you were asked to move a computer from one department to another for use by another user, what precautions would you take?
Suggested answers
Exercise 3
1. The files are slow to load because the read/write head must be moved over many sections of the disk to read all of the files segments. This also means more wear on the head positioning components.
2. You can use the file defragmentation program that is part of the Windows operating system. This makes all of the files contiguous. It will also optimise the files to place the most commonly used files in the part of the disk structure that is the fastest to access and the files that are not often used in the slowest part of the disk.
3. Your answer could include the following points:
• backing up is generally only done when the files are not currently in use. For this reason different parts of an organisations may back up files at a different times.
• generally, you back up as often as the outlay of time and effort to back up, is less than the time and effort taken to replace the files. For sensitive or financial data this may be very often, for less important documents it may be daily or even weekly.
• files that are sensitive or of an important nature could be backed up at lunchtime and close of business each day.
4. Generally files that have been backed up are removed from the place where the original files are stored. Banks often have a remote storage facility where backups are kept secure and safe from tampering or damage.
5. Scandisk checks for the file structure and ensures that all entries in the file allocation table match the reported values. It will attempt to reconcile irregular values to allow the file to be stored securely.
Defrag searches for non contiguous file fragments and moves them into adjoining sectors on the disk to speed up the loading of the files.
6. C
7. Your answer could include the following structure:
Root Directory
• Operating System
• User preferences
• Program Files
• Specific Applications
• Data Files
• Individual users/departments
8. Your answer could include the following precautions:
• ensure you informed the previous user that the machine is to be relocated
• perform a backup of the data files to ensure that files could be retrieved
• ensure that the computer is functioning correctly
• delete the data directories
• update the inventory documents
Practical Exercise Hardware Maintenance
In this exercise you will label the external features of a computer. You will need access to a computer to help you identify the parts. Some internet sites have been included in the answer section to help you learn more about computer hardware.
Systems Box
A typical computer system has a systems box which houses the motherboard, power supply, drives in drive bays, expansion slots and speaker. The case can be of a type that lies flat on the desk, called a desk top or one that is placed on edge, called a tower. This case is used to keep the components secure and isolated away from electrical interference.
It generally has a number of layers on the lid for strength and protection. A number of vents allow for a controlled airflow from the power supply and processor fan to keep the components at a satisfactory operating temperature.
Task 1
Label the features on the diagrams below from the following list: desk top case, tower case, 1.44 floppy disk drive, air vents, on/off switch, reset switch, front plane.
BACK PLANE
On the back of the systems box is the area where all of the peripheral devices are plugged in. This is called the BACK PLANE and has a number of interface cards that have been inserted into the expansion slots inside the case.
Suggested answers
Practical Exercise
Task 1
Task 2
Label the features on the diagrams below from the list. Back plane, keyboard and mouse sockets, fan outlet.
Suggested answers
Task 2
A Typical System
Generally most personal computer systems consist of the systems box, keyboard, mouse, monitor, printer, modem and commonly now a network interface card.
Practical task
• In groups, carefully disassemble one of the systems boxes that your teacher has prepared. You need to manage the task so that all components are put back in their correct placement when you reassemble the boxes.
• What method(s) will you use to ensure you know where the components are to be reconnected?
• Once everything has been removed, use a digital camera to capture an image of the components.
• Correctly reassemble all of the components of the systems box.
• Open the digital photograph in a paint program and add labels to the image(s) to identify all of the major components. You can use the internet or texts to find out any components you are unsure of. Try to label as many of the components on the motherboard as possible.
Suggested answers
Practical Task
You can find diagrams of motherboards at the following sites:
The Be Box Zone has a number of interesting bits of information as well as a diagram of a motherboard.
Loring Prest's Web site has a schematic of an older style computer motherboard.
A possible procedure for dismantling a system unit
• collect the correct tools for the type of computer you are working on
• ensure you are allowed to dismantle the machine
• clear an appropriate work space
• remove ALL connecting cable to ensure the unit is isolated from any power source
• remove screws or clips and note where they came from (especially important if there are different lengths or thread types)
• take note of where various cables and jumpers are connected and ESPECIALLY THEIR ORIENTATION. Masking tape and diagrams/digital images are good for recording where cables, etc go back.
• reassemble the system box, ensuring all components are where they originally came from.
Sample Project
Mario & Luigi's Internet Café
Mario has always wanted to own his own café with a super stainless steel, cappuccino machine and gelato of any imaginable flavour. Luigi is a computer whiz. Together, they have decided to open Mario & Luigi's Internet Café. Mario and Luigi have bought an empty office in downtown Suburbia. Now what do they do to turn an empty space in to an internet café ?
It is your job as a systems analyst to create a proposal to solve your new client's problem.
The proposal is to be in the form of a report. Include -
o Hardware requirements
- a printing service is required (customers pay a price per page)
o Software requirements
o Furniture required for customers to use the computer facilities
o Associated costs for - hardware, software, networking equipment, internet access, and systems analyst's contract fee.
o List as many products or services you can think of that will be required.
o Write maintenance procedures for all the computing facilities
o Ongoing customer support and service
o Draw a floor plan and network diagram
Create a log of your research. Include the date you accessed the information and list your sources such as internet sites, reference books and magazines
The dimensions of the office space are -
Suggested answers
Sample Project
Tips
Do a search on the internet to locate an internet caf site. Research their services and equipment.
A trip to an internet café is a good idea, have a talk to the owner to see how they went about setting up the system and the service. Find out about their maintenance procedures and schedule and then incorporate these details into your report.
When presenting your project you need to produce a technical report on the different aspects of your network design.
The main focus of your report should be on gathering the data from the clients and then researching to find appropriate costs and suppliers.
ICAITS014B Connect hardware peripherals
Connect hardware peripherals
Glossary
Other Resources
Sample Class Activities
Sample Projects
Overview
In general Hardware Peripherals can be classified in either internal/external or input/output/storage. Input devices relate to equipment that allows us to put data into the computer system for processing. After the data has been processed there is an output. This is a classical “input-process-output (IPO)” viewpoint about computers. However, the data may be stored, either prior or subsequent to processing, in a storage device. Of course there are devices, especially multi-function, that blur the distinction between these generalised areas of hardware peripherals.
CDROM
Compact Disk Read Only Memory – An optical 120mm diameter disk with 650megabytes capacity. It is used to store text, graphics, sound and video. The digital data is recorded in a spiral from the centre to the outermost edge
CMOS
Complimentary Metal-Oxide Semi-conductor: A low power using memory chip in personal computers the holds time, date and other critical system startup information
DMA
Direct Memory Access: A method of allowing the peripherals to bypass the processor and send blocks of data to a secured memory location. This can speed up data transfer operations enormously.
driver
Operating systems and applications use a general system call to operate hardware devices. The driver is a software routine that translates it into the specific instructions needed to control the hardware device.
DVD
Digital Versatile Disc: 120mm optical disc with a capacity of 4.7 gigabytes. Expected to replace CDROM.
Firewire
A fast (up to 50megabyes per second) serial bus with support for 63 hot swap, plug and play devices. Has the potential to replace serial, parallel, IDE and SCSI Hard disk type interfaces.
IRQ
Interrupt Request: Hardware devices can gain some processor attention by sending a signal via the interrupt request line. Early devices required some knowledge of interrupts to avoid conflicts. Plug and Play now handles the setup of a new device’s communication channels with the rest of the system including the IRQ.
PS/2
A 6 pin mini DIN socket on most computers used for the mouse and keyboard.
RS232
Recommended Standard 232C: now ratified as the EIA-232 standard, which is used by all dial-up modems. The serial port may be either 25pin or 9pin D shell.
USB
Universal Serial Bus: An external peripheral interface with a 12Mb transfer rate. It supports up to 127 hot swappable, plug and play devices. It is expected to replace the standard serial and parallel ports
Other resources
• whatis.techtarget.com/ - General purpose site for Information Technology related definitions
• www.webopedia.com/ - General purpose site for Information Technology related definitions
• peripherals.about.com/cs/findingdrivers/ - A site for software drivers targeted to peripherals devices
• www.windrivers.com/ - A site for Microsoft Windows related software drivers
• www.drdriver.com/ - A site for device drivers
Sample class activities
Activity 1
In the examples of peripherals below see if you can determine the industry sector (office, home, manufacturing, retail) that the peripherals may characteristically be used in:
Input: Keyboard, mouse, joystick, microphone, trackball, graphics tablet, glidepad, network interface card, barcode reader, scanner, touch screen, sensor, digital camera
Output: Speakers, monitor, printer, network interface card, force feedback device (mouse, headphones, steering wheel, chair, vest, joystick), actuator.
Storage: Floppy disk drive, hard disk drive, optical based disks (CD, DVD etc..), flash cards, memory stick.
Activity 2
Match the port with the description
The Port Match Choice Description
1 Monitor
2 Power in
3 RJ45
4 Voltage selector switch
5 Microphone / speakers
6 Bayonet Network Connector
7 PS/2 Mouse
8 Universal Serial Bus
9 “Firewire” IEEE1394
10 Joystick / MIDI
Activity 3
• Name the following mainboard expansion slots, their speed in megahertz and how many data bits per clock cycle they transfer.
Name Speed Data bits
PCI
AGP
ISA
•
• Describe the OH&S precautions you would undertake while working inside a computer
• How many bytes are there in 2 Kilobytes (2K)?
• There are three (3) connectors on a 34 pin ribbon cable with a twist in the cable between the 2nd and 3rd connectors. At which connector would you put floppy B and floppy A.
• Demonstrate how you would enter the CMOS and adjust the computer for the use of a Plug and Play operating system
• Demonstrate how you would reserve IRQ 5 for a legacy Sound Blaster 16 audio card in the CMOS.
• Demonstrate how you would set the Cylinders Heads and Sectors for a non-standard hard disk drive within the CMOS.
• Show how you would alter the IRQ, DMA and I/O port settings of hardware devices within Windows
• How would you find pin1 of an internal hard or floppy disk ribbon cable?
• On an older style AT power supply there are two (2) flat four (4) socket connectors that plug into the mainboard. How could you tell which way they should be orientated?
• If you were installing two (2) hard drives onto the same IDE ribbon cable how would you ensure that they would work together.
Sample projects
1. Your friend has decided to buy a computer and a salesperson has faxed them a quote. The computer on the fax was described as: PIII 800EB CPU, 128MB PC-133 SDRAM, 30GB HDD, 1.44FDD, 17” NI XGA monitor, 48x CDROM, 32MB 3D AGP graphics card, 12mths RTB warranty. $1895 incl GST Your friend has asked you to explain each of the abbreviations.
2. Create an installation manual targeted to the advanced user for a new graphics card. Use the following as a general guideline.
o Determine the client’s requirements.
o Confirm the minimum specifications required for new device
o Obtain the latest drivers and applications software from the manufacturers web site
o Backup, as a minimum, the critical system files
o Uninstall previous device or reset the device to a compatible state
o Set any jumpers/switches/terminators as per the peripheral documentation
o Physically install new device
o Restart computer and install the drivers and software supplied with the device. Operationally test the device
o Apply the latest driver from the web site.
o Operationally test the device again
o Register the product
o Update the asset inventory
o Review the hardware and software maintenance procedures
o Train any users.
o Confirm with the client that their requirements have been met.
ICAITU005C Operate computer hardware
Operate computer hardware
Introduction
On completion of this unit, learners should be competent in determining, selecting and correctly operating basic computer hardware.
Learners should have the ability to:
1. Use appropriate office peripherals
2. Operate and maintain a range of hardware
3. Use a keyboard and equipment
Use appropriate office peripherals
What should I know?
Students should be able to
• identify the functions of office peripherals
• determine the requirements of tasks
• select appropriate hardware to perform a task
• use hardware to produce required outcome.
What does a computer do?
What is the role of software in a computer system?
What's in a computer system?
Exercise 1 - Explain the following specifications
Exercise 2 - Specify a machine suitable for video editing
How can I connect more equipment to my computer?
Exercise 3 - Computer ports
What equipment can I connect?
Exercise 4 - Select appropriate hardware
How do I connect equipment to my computer system?
Exercise 5 - Peripheral installation
How do I know what components and equipment are installed in a computer sytem using operating system tools?
Exercise 6 - Examine your computer system
How do I know what components and equipment are installed in a computer system using software?
What does a computer do?
 A computer system is designed to accept INPUT from devices such as keyboards and mice.
A computer system is designed to accept INPUT from devices such as keyboards and mice.
It takes this information and will PROCESS the data.
The next step is to then present the OUTPUT of this processing in the required format to an output device such as a printer or monitor.
To complete these tasks, computer systems have:
• hardware - physical devices that make up the system
• software - programs designed to process the data
• data.
What is the role of software in a computer system?
There are three main types of software that a computer system uses:
• BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) which is stored on the system ROM (Read Only Memory)
• Operating System or OS
• Application software such as Microsoft Office
At Start up 
1. BIOS tests essential hardware and performs routine tasks. This process is called the boot process.
2. BIOS passes control of the computer system to the operating system.
3. The operating system then performs more start up tasks.
During operation 
1. The user interacts with both the operating system and the application software.
2. For the user or the application software to access a piece of hardware such as a printer, the request is passed through either the BIOS or software called device drivers. Devices such as memory and floppy drives are controlled by BIOS. Devices such as printers and graphics cards will use a device driver.
What's in a computer system?
Read an explanation of each component and an example specification of each component.
Desktop
Processor Intel® Pentium® 4 with HT Technology 2.8GHz CPU
Operating system Microsoft® Windows® XP Home Edition Operating system
Memory 512MB DDR-SDRAM Memory
Hard drive 80GB Hard Drive 7200 Storage drives
Monitor 17" Flat Panel Monitor (17.0"v.i.s.) Video
Optical device CD-RW Combo Drive 48x 24x Optical devices
Video card 128MB DDR nVidia® GeForce® FX 5200 Video
Sound card Sound Blaster® Live!TM 5.1 Sound Card Sound
Speaker PC Stereo Speakers Sound
Keyboard Keyboard Keyboard
Mouse Mouse Mouse
Complete the following two exercises. Students should be able to select appropriate hardware for computer systems and write specifications.
Australian PC World has buying guides for most computer components and peripherals, if you would like to view more detailed information.
Exercise 1 - Explain the following specifications
You are working for a small company that is looking to upgrade their computer systems and the following cryptic quote has been received. Rewrite the quote so that the company's accountant can better understand what equipment is being offered.
P4 2.8Ghz, 512 MB DDR-SDRAM, 40GB 7200 HDD, 52x CD-ROM, 17" LCD,
integrated sound, video and network with WinXP Pro $1500
Suggested answers - Exercise 1
Exercise 1 - Suggested answer
You are working for a small company that is looking to upgrade their computer systems and the following cryptic quote has been received. Rewrite the quote so that the company's accountant can better understand what equipment is being offered.
P4 2.8Ghz, 512 MB DDR-SDRAM, 40GB 7200 HDD, 52x CD-ROM, 17" LCD, integrated sound, video and network with WinXP Pro $1500
Suggested answer:
The computer that we are quoting on has the following specifications:
Specification
CPU Intel Pentium 4 speed 2.8Ghz
Memory 512 MB DDR-SDRAM
Hard Drive 40 GB rotational speed 7200 rpm
CD speed 52x, read only
Monitor 17" flat panel LCD
Sound, Video, Network interface integrated on the motherboard
Operating system Microsoft Windows XP Professional
Also included in the system are: floppy drive, mouse and keyboard.
Exercise 2 - Specify a machine suitable for video editing
The company accountant is also interested in purchasing a computer for home use and wants to be able to edit videos made from the new video camera that they have just bought.
• Is the quoted system suitable for this use?
• What specifications would you suggest to the accountant to suit this purpose?
Suggested answers - Exercise 2
Exercise 2 - Suggested answer
The computer system that was quoted is suitable for use for general computing such as word processing and web surfing but would not be recommended to use with video editing.
To meet the accountant’s requirements I would make the following recommendations:
Original Specification Proposed Specification
CPU Intel Pentium 4 speed 2.8Ghz Intel Pentium 4 speed 2.8Ghz minimum
Memory 512 MB DDR-SDRAM 1 GB DDR-SDRAM
Hard Drive 40 GB 7200 100 GB minimum 7200 rpm
Video and audio files require a lot of hard drive space.
You can store 4.5 minutes of raw, or uncompressed video per GB of hard drive space.
A 60 minute move requires about 14GB.
CD speed 52x, read only A CD-W is needed to record a CD.
Depending on the budget you could upgrade to:
DVD-R: to be able to play DVDs.
DVD burner: to be able to record DVDs.
I would recommend a DVD burner.
Monitor 17" flat panel 17" flat panel
Sound, Video, Network interface integrated on the motherboard For the video editing, I would not recommend the use of integrated sound and video. Video: AGP card with minimum 64MB memory.
Network interface: integrated.
Camera Interface None Firewire (1394) interface card (if required by camera)
Operating system Microsoft Windows XP Professional Microsoft Windows XP Professional
How can I connect more equipment to my computer?
Most of the peripheral devices that you can connect to your computer system are connected externally through different ports.
Ports are identified by:
• their shape
• number of pins
• and whether male or female (in the descriptions below, the connectors are as ON the computer system)
Place mouse over images to see what equipment connects to these ports
Picture Description
Serial port
• DB connector
• can be 9 or 25 pin male
• usually two on a computer system labelled COM1 and COM2
• only one device per port
Parallel port
• DB connector
• 25 pin female
• usually one on a computer system labelled LPT1
only one device per port, but devices can be daisy chained (only one can be used at a time)
PS/2 port
• 6 pin mini DIN connector
• usually two on a computer system
• typically 2 or 4 ports on PC
hot swappable (devices can be attached while the computer is powered)
can connect up to 127 devices
• can supply power to devices
• two varieties of USB
1. USB 1.1 - 12 Mbit/sec
2. USB 2.0 - 480 Mbit/sec
IEE1394 high performance serial bus (commonly known as Firewire)
• typically requires the installation of an internal adapter card for a desktop computer system
• Hht swappable
can connect up to 63 devices
• high data transfer rates of 400Mbps (in 1394a) and 800Mbps (in 1394b).
Exercise 3 - Computer ports
Students should be able to select the most appropriate hardware for the task. To do this students should be able to identify the ports that are used to connect computer peripherals.
Complete the following table.
Question Number Question Answer
1. Give a brief definition of the term computer port.
2. Name two devices that might use a USB connection.
3. Your company is looking to purchase a new modem. Would you recommend that they purchase a modem with a serial or USB connection?
4. What features of the IEE1394 (Firewire) port make it suitable for use with video recorders?
5. Your desktop computer system has two USB ports, but you have four USB devices - printer, modem, web camera and keyboard. What would you recommend?
Exercise 3 - Suggested answers
Question number Question Suggested answer
1. Give a brief definition of the term computer port. A physical connector usually on the back of the computer that allows a cable from a peripheral device such as a printer to connect to the computer system.
2. Name two devices that might use a USB connection. • keyboard
• mouse
• modem
• scanner
• printer
• digital cameras
3. Your company is looking to purchase a new modem. Would you recommend that they purchase a modem with a serial or USB connection? You would recommend the USB connection as it is the latest. (Some new computer systems do not even have a serial port.)
4. What features of the IEE1394 (Firewire) port make it suitable for use with video recorders? • Hot swappable
• High data transfer rates of 400Mbps (in 1394a) and 800Mbps (in 1394b).
5. Your desktop computer system has two USB ports, but you have four USB devices - printer, modem, web camera and keyboard. What would you recommend? As USB devices are hot swappable, you unplug and plug devices as required. A better solution would be to purchase a USB hub to allow all devices to be connected at the same time.
What equipment can I connect?
There is a wide variety of peripheral devices that can be connected to a computer system. Broadly, they fit into one of the following three categories.
Input devices
• keyboard
• mouse
• scanner
• digital camera
• microphone
Output devices
• monitor
• printer
• modem (a modem is really both an input and output device)
• speakers
Storage devices
• USB memory sticks
• Large capacity disk drives such as zip drives
Exercise 4 - Select appropriate hardware
Students should be able to select the most appropriate hardware for the task.
Suggest the most appropriate peripheral device that will be suitable for the given task.
Task Suitable peripheral
Connect to the Internet
Capture digital images
Store large amounts of data in a portable format
Capture an audio signal
Convert an image on paper to a digital image
Exercise 4 - Suggested answers
Suggest the most appropriate peripheral device for the given task.
Task Suitable peripheral
Connect to the Internet. modem
Capture digital images. digital camera
Store large amounts of data in a portable format. USB memory stick or large capacity disk drive such as a Zip drive
Capture an audio signal. microphone
Convert an image on paper to a digital image. scanner
How do I connect equipment to my computer system?
ICAITS014B
Connect hardware peripherals
Glossary
Other Resources
Sample Class Activities
Sample Projects
Overview
In general Hardware Peripherals can be classified in either internal/external or input/output/storage. Input devices relate to equipment that allows us to put data into the computer system for processing. After the data has been processed there is an output. This is a classical “input-process-output (IPO)” viewpoint about computers. However, the data may be stored, either prior or subsequent to processing, in a storage device. Of course there are devices, especially multi-function, that blur the distinction between these generalised areas of hardware peripherals.
CDROM
Compact Disk Read Only Memory – An optical 120mm diameter disk with 650megabytes capacity. It is used to store text, graphics, sound and video. The digital data is recorded in a spiral from the centre to the outermost edge
CMOS
Complimentary Metal-Oxide Semi-conductor: A low power using memory chip in personal computers the holds time, date and other critical system startup information
DMA
Direct Memory Access: A method of allowing the peripherals to bypass the processor and send blocks of data to a secured memory location. This can speed up data transfer operations enormously.
driver
Operating systems and applications use a general system call to operate hardware devices. The driver is a software routine that translates it into the specific instructions needed to control the hardware device.
DVD
Digital Versatile Disc: 120mm optical disc with a capacity of 4.7 gigabytes. Expected to replace CDROM.
Firewire
A fast (up to 50megabyes per second) serial bus with support for 63 hot swap, plug and play devices. Has the potential to replace serial, parallel, IDE and SCSI Hard disk type interfaces.
IRQ
Interrupt Request: Hardware devices can gain some processor attention by sending a signal via the interrupt request line. Early devices required some knowledge of interrupts to avoid conflicts. Plug and Play now handles the setup of a new device’s communication channels with the rest of the system including the IRQ.
PS/2
A 6 pin mini DIN socket on most computers used for the mouse and keyboard.
RS232
Recommended Standard 232C: now ratified as the EIA-232 standard, which is used by all dial-up modems. The serial port may be either 25pin or 9pin D shell.
USB
Universal Serial Bus: An external peripheral interface with a 12Mb transfer rate. It supports up to 127 hot swappable, plug and play devices. It is expected to replace the standard serial and parallel ports
Other resources
• whatis.techtarget.com/ - General purpose site for Information Technology related definitions
• www.webopedia.com/ - General purpose site for Information Technology related definitions
• peripherals.about.com/cs/findingdrivers/ - A site for software drivers targeted to peripherals devices
• www.windrivers.com/ - A site for Microsoft Windows related software drivers
• www.drdriver.com/ - A site for device drivers
Sample class activities
Activity 1
In the examples of peripherals below see if you can determine the industry sector (office, home, manufacturing, retail) that the peripherals may characteristically be used in:
Input: Keyboard, mouse, joystick, microphone, trackball, graphics tablet, glidepad, network interface card, barcode reader, scanner, touch screen, sensor, digital camera
Output: Speakers, monitor, printer, network interface card, force feedback device (mouse, headphones, steering wheel, chair, vest, joystick), actuator.
Storage: Floppy disk drive, hard disk drive, optical based disks (CD, DVD etc..), flash cards, memory stick.
Activity 2
Match the port with the description
The Port Match Choice Description
1 Monitor
2 Power in
3 RJ45
4 Voltage selector switch
5 Microphone / speakers
6 Bayonet Network Connector
7 PS/2 Mouse
8 Universal Serial Bus
9 “Firewire” IEEE1394
10 Joystick / MIDI
Activity 3
• Name the following mainboard expansion slots, their speed in megahertz and how many data bits per clock cycle they transfer.
Name Speed Data bits
PCI
AGP
ISA
•
• Describe the OH&S precautions you would undertake while working inside a computer
• How many bytes are there in 2 Kilobytes (2K)?
• There are three (3) connectors on a 34 pin ribbon cable with a twist in the cable between the 2nd and 3rd connectors. At which connector would you put floppy B and floppy A.
• Demonstrate how you would enter the CMOS and adjust the computer for the use of a Plug and Play operating system
• Demonstrate how you would reserve IRQ 5 for a legacy Sound Blaster 16 audio card in the CMOS.
• Demonstrate how you would set the Cylinders Heads and Sectors for a non-standard hard disk drive within the CMOS.
• Show how you would alter the IRQ, DMA and I/O port settings of hardware devices within Windows
• How would you find pin1 of an internal hard or floppy disk ribbon cable?
• On an older style AT power supply there are two (2) flat four (4) socket connectors that plug into the mainboard. How could you tell which way they should be orientated?
• If you were installing two (2) hard drives onto the same IDE ribbon cable how would you ensure that they would work together.
Sample projects
1. Your friend has decided to buy a computer and a salesperson has faxed them a quote. The computer on the fax was described as: PIII 800EB CPU, 128MB PC-133 SDRAM, 30GB HDD, 1.44FDD, 17” NI XGA monitor, 48x CDROM, 32MB 3D AGP graphics card, 12mths RTB warranty. $1895 incl GST Your friend has asked you to explain each of the abbreviations.
2. Create an installation manual targeted to the advanced user for a new graphics card. Use the following as a general guideline.
o Determine the client’s requirements.
o Confirm the minimum specifications required for new device
o Obtain the latest drivers and applications software from the manufacturers web site
o Backup, as a minimum, the critical system files
o Uninstall previous device or reset the device to a compatible state
o Set any jumpers/switches/terminators as per the peripheral documentation
o Physically install new device
o Restart computer and install the drivers and software supplied with the device. Operationally test the device
o Apply the latest driver from the web site.
o Operationally test the device again
o Register the product
o Update the asset inventory
o Review the hardware and software maintenance procedures
o Train any users.
o Confirm with the client that their requirements have been met.
Once you have determined that you require a peripheral device for a computer system, you would need to complete the following tasks:
1. Identify the requirements for the peripheral, select the peripheral and make sure that your computer system meets any minimum system requirements.
Compare product features from a range of manufacturers and compare prices from several suppliers.
1. Document your purchase recording details such as purchase date, supplier serial number, warranty details and any software received.
2. READ THE MANUAL.
3. In general, you would connect the peripheral to your computer system using the correct port and the install device drivers and any additional software. Some USB devices require that the software is installed before the device is connected.
4. Test your device.
Exercise 5 - Peripheral installation
You have just purchased a new printer.
1. Give three possible sources that you could use to find the appropriate device driver.
2. The printer is "plug and play". Explain what this means.
Suggested answers - Exercise 5
Exercise 5 - Suggested answers
You have just purchased a new printer.
1. Give three possible sources that you could use to find the appropriate device driver.
2. The printer is "plug and play". Explain what this means.
1. Three possible sources are:
• the installation CD that comes with the printer
• the manufacturer's web site (this would ensure that you are using the latest driver)
• your operating system.
2. "Plug and play" devices are devices that will work together with the operating system to automatically configure themselves. The BIOS must also support "plug and play"
How do I know what components and equipment are installed in a computer system using operating system tools?
The following screen shots have been taken on a computer using Microsoft Windows XP as the operating system. The instructions and screen shots may be slightly different depending on your operating system.
CPU, memory, operating system
• Right click My Computer and select Properties from the drop down menu.
This shows:
• the CPU is an Intel(R) Pentium(R) 2.4 Ghz
• there is 512MB of RAM
• the operating system is Windows XP Professional.
Storage capacity
• At start select My Computer.
• Right click the drive you want to find information on.
• Select Properties and a screen similar to the following will appear.
• This shows the drive has a total capacity of 29.2 GB of which 11.1 GB has been used.
Installed devices
(You may need to vary these steps for other operating systems. Use Help to find the Device Manager)
• In Windows XP, at start select Control Panel, then double click System.
• Select the Hardware tab and then double click the Device Manager button.
Device Manager lists all the hardware devices installed on your computer.
Also if a device has a problem a symbol also appears to indicate the type of problem:
• A black exclamation point (!) on a yellow field indicates the device is in a problem state.
• A red "X" indicates a disabled device. A disabled device is a device that is physically present in the computer, but does not have a driver loaded. Look at the Network adapter symbol for an example.
• A blue "i" on a white field on a device resource in Computer properties indicates that the Use Automatic Settings feature is not selected for the device and that the resource was manually selected.
Exercise 6 - Examine your computer system
To install a new peripheral device or a new software application, it is important that you know what components are installed in your computer system. Then you can decide if your system meets the minimum system requirements.
Print a copy of the following table. Use the operating system tools described in How do I know what components and equipment are installed in a computer system using operating system tools? to complete the table for the computer system that you are currently using.
Component Description
Operating system
Memory
CPU
Storage capacity
C:
D:
Installed devices
Display adapter
DVD/CD-Rom drive
Modem
Printer
Do any installed devices have a problem?
If so, describe the problem
Suggested answers - Exercise 6
Device driver
A device driver is a program that controls a device such as a printer or graphics card.
Many drivers, such as the keyboard driver, come with the operating system. For other devices, you may need to load a new driver when you connect the device to your computer.
A driver acts like a translator between the device and programs that use the device. Each device has its own set of specialised commands that only its driver knows. In contrast, most programs access devices by using generic commands. The driver, therefore, accepts generic commands from a program and then translates them into specialized commands for the device.
How do I know what components and equipment are installed in a computer system using software?
If you require more detailed information about the installed hardware on your computer system, you will need to use software known as a diagnostic utility. These programs are designed to report extensively on the installed hardware and also can incorporate additional features such as hardware testing.
There are a great number of utilities available. Some of the commonly used are shown below.
Norton Systemworks
One of the most common utilities was Norton Utilities. This is now available as part of Symantec’s Norton SystemWorks™ 2004.
SiSoft Sandra
SiSoftware Sandra (the System ANalyser, Diagnostic and Reporting Assistant) is an information and diagnostic utility. It should provide most of the information software and other devices, whether hardware or software.
You can download Sandra Standard free for personal/educational use. Go to the download page. sample screen shot
Microscope 2000
Micro-Scope diagnostic software is a collection of PC diagnostics routines, benchmarking and other tools for troubleshooting PC computer hardware.
Belarc Advisor
The Belarc Advisor builds a detailed profile of your installed software and hardware, including Microsoft Hotfixes, and displays the results in your web browser.
The license associated with the Belarc Advisor product allows for free personal use only.
Operate and maintain a range of hardware
What should I know?
Students should be able to:
• operate a range of hardware equipment to complete routine tasks
• determine required hardware consumables and replace.
Exercise 1 - How do I format a floppy disc?
What consumables does a printer need?
Exercise 2 - Researching printer cartridges
Exercise 3 - What other consumables will I need for my computer system?
What happens when I send a print job to the printer?
Exercise 4 - Printer settings
How do I use a networked printer?
Exercise 5 - Using a networked printer
Exercise 1 - How do I format a floppy disc?
Students should be able to format a floppy disk using different switches or options.
Formatting a disk prepares the disk for reading and writing.
Information on a disk is laid down on tracks, which are divided into sectors. Floppy disks have two sides. Each side has 40 tracks with nine sectors per track.
When you format a disk, the operating system erases all bookkeeping information on the disk, tests the disk to make sure all sectors are reliable, marks bad sectors (that is, those that are scratched), and creates internal address tables that it later uses to locate information.
If you are deleting all files to reuse the floppy disk, formatting the disk is a better option, as a full format will delete all files and also check the disk. New floppy disks are pre-formatted.
For this exercise you will need a blank floppy disk inserted into A: drive.
Part 1 - Using the GUI tools
The following screen shots have been taken on a computer using Microsoft Windows XP as the operating system.
The instructions and screen shots may be slightly different depending on your operating system.
• Double click My Computer on your desktop.
• Right click the 3 1/2" Floppy (A:).
• Select Format from the drop down menu. The window shown to the right appears.
To get information about any option double click the question mark and drag it to an option.
Use the Help to answer the following questions.
What is the difference between a quick format and a normal format?
What is the purpose of the volume label?
What is the purpose of an MS-DOS start up disk?
Suggested answers - Exercise 1- GUI
Exercise 1 - Suggested answers
Part 1 - Using the GUI tools
What is the difference between a quick format and a normal format?
What is the purpose of the volume label?
What is the purpose of an MS-DOS startup disk?
The MS-DOS startup disk allows the system to boot into an MS-DOS prompt. The disk contains no additional tools.
Part 2 - Using the command prompt
At Start select All Programs and then Accessories. Select Command Prompt.
At the prompt, type format /?. This displays all the switches that can be used with the format command.
What consumables does a printer need?
Consumable items are items that need to be replaced during the operating life of a printer.
Paper
Printers can accept a variety of media, such as paper, labels and transparencies. Common paper sizes are:
• A4 - the most common paper size in Australia for printing documents (210 x 297 mm)
• Letter - the most common paper size in the USA (215 x 297)
• Legal - 215 x 355 mm
It is important to check your printer settings because printer software will often use the letter paper size as a default, rather than A4.
All stocks of printer media should be stored in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations, particularly with respect to temperature and humidity.
Toner cartridges
Laser printers have a toner cartridge that will need replacing. Typically the printer will issue a warning that the cartridge needs replacing. If faded or light areas appear on a printed page, this is also an indication that the toner needs replacing.
Before replacing the printer cartridge, you can remove the toner cartridge from the printer and shake it gently from side to side to redistribute the toner. Print a test page to see if the printing quality has improved.
Operating the printer on low toner levels is to be avoided as the printer drum can be damaged.
Do not remove the toner cartridge from its package until you are ready to use it. An unopened cartridge has a shelf life of two to three years, but opened, the shelf life is six months.
To replace a toner cartridge refer to the user manual for your particular printer.
In general, the steps are as follows:
Turn off the printer at the power outlet.
Open the printer door and remove the old printer cartridge.
Remove the toner cartridge from the packaging and gently shake.
Most cartridges have a plastic tab that seals the cartridge for storage.
Pull the tab until the tab and tape are removed.
Insert the toner into the printer and close the door.
Print a test page.
What do I do with the used cartridges?
Some manufacturers have cartridge return programs where you can return your empty cartridges for recycling. Alternatively Planet Ark has introduced a program called Cartridges 4 Planet Ark to facilitate the recycling of cartridges.
Inkjet Printers
Inkjet printers have one or more inkjet cartridges that will need to be replaced. Typically you will need to replace the cartridges when the quality of a print is poor. Some printers will also give a visual indication of the levels of ink remaining in the cartridge.
Typically an inkjet printer will have four cartridges: black and three for colour printing.
To replace an inkjet cartridge refer to the user manual for your particular printer.
In general, the steps are as follows:
Leave the printer on.
Open the printer cover and the cartridge moves to the centre.
Remove the existing cartridge.
Remove the protective tape from the new cartridge.
Install the cartridge.
Some printers will then lead you through a series of steps to ensure that the print heads are aligned.
Print a test page.
Exercise 2 - Researching printer cartridges
Students need to be able to determine required hardware consumables and replace them.
Your company uses the following printer:
• Hewlett Packard (HP) monochrome laser printer model HP LASERJET 4050N for general document printing.
You have looked at your User Manual for the printer and have found you need to use the following replacement cartridge:
• HP LASERJET 4050N - Part No. C4127X.
As your company has ten of these printers, you decide to research the cost of the cartridges.
Compare prices of at least two on the following sites for the cost of the cartridge.
Approximately how many pages will this cartridge print?
Paw products
ISWH (Software Warehouse)
Harris Technologies
Suggested answers - Exercise 2
Exercise 2 - Suggested answers
Your company uses the following printer:
• Hewlett Packard (HP) monochrome laser printer model HP LASERJET 4050N for general document printing.
You have looked at your user manual for the printer and have found you need to use the following replacement cartridge:
• HP LASERJET 4050N - Part No. C4127X.
As your company has ten of these printers, you decide to research the cost of the cartridges.
1. Compare prices of at least two on the following sites for the cost of the cartridge.
At the time of writing (May 2004), prices were from about $160.00 to $220.00.
2. Approximately how many pages will this cartridge print?
10 000 pages.
Exercise 3 - What other consumable items will I need for my computer system?
In the section above you have looked at the consumables required for printers. Other devices will also require consumables.
List four other consumables that you may require for your computer system.
Suggested answers - Exercise 3
Exercise 3 - Suggested answers
In the section above you have looked at the consumables required for printers. Other devices will also require consumables.
List four other consumables that you may require for your computer system.
Item no Component Consumable required
1 floppy drive floppy disks, usually purchased in packs of 10
2 CD writer recordable CDs to suit
3 back up tape drive tape back up media to suit
4 various Cleaning products are available for general computer system cleaning, monitors, floppy drives and CD drives.
What happens when I send a print job to the printer?
Step 1 - When the user asks the application to print a document, it sends the document to the operating system so that the application can be released from the printing process as soon as possible.
Step 2 - The operating system places the job in a print queue where print jobs can accumulate. Print jobs are then set to the printer for printing.
This process of queue printing is called spooling.
If your computer system has only one printer installed, it will be the default printer. If there is more than one printer installed, one printer will need to be set as the default printer which is denoted by a white tick in a black circle.
When the user goes to print from an application, the default printer will be the first option.
Exercise 4 - Printer settings
Students should be able to use a variety of printer settings.
Different printers will have different settings that can be changed. You will need to refer to the user manual for your specific printer. The following screen shot was taken using an Epsom Stylus C43 printer.
Questions:
1. Describe the difference between portrait and landscape orientation.
2. What settings would need to be changed if the user wanted to print photos?
3. If you have a printer installed on your computer system, look at the printer properties. (Right click on the printer and then select Properties from the drop down menu.) What are some other properties that can be set for your printer?
Suggested answers - Exercise 4
Exercise 4 - Suggested answers
1. Describe the difference between portrait and landscape orientation.
Portrait is the more usual orientation and will print the page vertically. Landscape will print the page horizontally.
2. What settings would need to be changed if the user wanted to print photos?
You would need to change the quality type to Photo and change the Paper Options type to the correct type of photo paper.
3. If you have a printer installed on your computer system, look at the printer properties. (Right click on the printer and then select Properties from the drop down menu.) What are some other properties that can be set for your printer?
There are many properties that can be set. Some include:
o port connected to
o spooling options
o whether the printer is shared over the network
How do I use a networked printer?
You will find more information about networks and network printing at ICAITS121A - Administer network peripherals . This is an ELECTIVE module.
Computer peripherals are too expensive for companies to provide to each computer. Most companies will have their computers connected together in a computer network that allows users to share the peripheral devices such as printers and also to share data and files.
STAND ALONE SYSTEM NETWORKED SYSTEM
HUB - hardware device used to connect network cabling and PCs.
Server - A computer that manages network resources.
A computer network has many advantages over a stand-alone computer system:
• Peripherals can be shared.
• Files and data can be shared.
• Administration of users and file security can be centralised.
• Back up of important data can be centralised.
A server used to share files is known as a file server.
When computers are networked, it will be the function of one or more people to act as a system administrator. Some functions that a system administrator is responsible for are:
• creating user accounts
• allowing user access to resources such as printers and files
• installing system-wide software.
The system administrator will allocate to each user a username (eg FSmith) and a password. Depending on company policy, usually the user will be prompted the first time that they log in to the network to change their password.
Typically users are organised into groups to simplify the administration of the network. For example, in a school teachers and students would be placed into different groups because they will have different levels of access to the resources.
The system administrator can assign different levels of security to users.
For files, typical settings for file security are given below. The exact level of access will depend on what operating system is being used:
• none
• modify
• read and execute
• view folder contents
• write to the file or folder
• read-only access
What is a printer pool?
For companies with a high volume of printing, setting up a printer pool is a good idea. A printer pool has two or more identical printers with one set of printer software.
When a document is sent to the printer pool, the first available printer receives and prints it. This configuration maximizes print device use while minimizing the time users wait for documents.
Another advantage of a printer pool is that if one printer is malfunctioning, for example it has a paper jam, the user can still print, as the print job will go to the next printer in the pool.
The user sees the printer pool as a single printer.
Exercise 5 - Using a networked printer
In a business environment printers are often networked. Students need to be able to operate a networked printer to complete routine tasks.
Complete the following table.
Question Answer
1. What are two advantages of using a networked printer?
2. To be able to use a networked printer, users must have access to networked resources. How does a user gain this access?
3. Apart from printers, what resources are commonly shared on a network?
4. The printers in a printer pool must be different. True / False?
5. A company has four printers connected in a printer pool. How does the user see the four printers when they go to print a document?
Suggested answers - Exercise 5
Exercise 5 - Suggested answers
1. What are two advantages of using a networked printer?
o Allows an expensive resource to be shared between users.
o Allows central administration of the resource.
2. To be able to use a networked printer, users must have access to networked resources. How does a user gain this access?
The system administrator will assign:
o Username
o Password.
3. Apart from printers, what resources are commonly shared on a network?
o Files and data.
4. The printers in a printer pool must be different. True / False?
o False:
printers in a printer pool must be the same or use the same printer driver.
5. A company has four printers connected in a printer pool. How does the user see the four printers when they go to print a document?
o The user will only see one printer in the print dialog box.
Use a keyboard and equipment
What should I know?
Students should be able to follow
Occupational Health and Safety regulations carry out keyboarding in accordance with organisational guidelines on speed and accuracy.
Links
What's the best position for my monitor?
Exercise 1
How do I learn to use the keyboard?
Links
You will find more information about Occupational Health and Safety regulations at ICAITU004B Apply Occupational Health and Safety procedures.
Ergonomic Workstation Links
The Australian Government National Occupational Health and Safety Commission has guidelines to workplace layout and design.
The University of Western Australia has a guide to working comfortably with computers.
IBM Computing has a site devoted to helping you use your personal computer comfortably, providing extensive ergonomic information.
There is an Australian Standard AS 3590 - 1990 Screenbased workstations, part 2 that makes recommendations about workstations
What's the best position for my monitor?
The following notes have been compiled from the above sources on ergonomics and workstations.
Monitor location
• Set the eye to screen distance at the distance that permits you to most easily focus on the screen. Usually this will be within an arm's length or a distance of about 630 mm.
• Set the height of the monitor so that the top of the screen is below eye level and the bottom of the screen can be read without a marked inclination of the head. Usually this means that the centre of the screen will need to be near shoulder height.
• Set the contrast and brightness of the screen at a comfortable level.
• As the light in the room changes, adjust the contrast and brightness, if necessary.
• Clean your screen, anti-glare filter and eyeglasses on a regular basis.
• Consult your vision care specialist if you experience eye fatigue or discomfort.
Lighting
• Place monitors to the side of the light source/s, not directly underneath.
• Try to site desks between rows of lights. If the lighting is fluorescent strip lighting, the sides of the desks should be parallel with the lights.
• Try not to put the screen near a window. If it is unavoidable ensure that neither the screen nor the operator faces the window.
Exercise
Read the Australian Government National Occupational Health and Safety Commission guidelines to workplace layout and design.
List six items that should be considered when designing the physical layout of a workstation.
Suggested answers - Exercise 1
Exercise 1 - Suggested answers
List six items that should be considered when designing the physical layout of a workstation.
1. Are desks, benches and chairs suitable for the people using them and for the tasks they are performing? Poorly designed chairs, which cannot be adjusted for height and to support your lower back, can cause back pain. Desks which are not ergonomically designed and adjustable to accommodate a range of heights can also cause discomfort and increase the risk of OOS and other injuries.
2. Are passages and exits kept clear at all times? Accidents can be caused by poor housekeeping; for examples boxes stacked near workstations, or in passages and doorways, or equipment left lying on the floor.
3. Is equipment with dangerous moving parts properly guarded? Unguarded equipment is a frequent cause of workplace injuries and fatal accidents.
4. Are electric cords kept clear of walkways and other areas where people could trip over them? Are cords and extension leads kept away from areas where they could get wet?
5. Are suitable lifting and carrying devices such as hoists and trolleys supplied? Many lifting tasks require the use of these devices.
6. Are items which must be manually lifted and carried stored and worked on at a suitable height? Well designed storage areas and work areas can significantly reduce the amount of bending, twisting and lifting that you need to do to carry out your tasks. Reducing these activities will also reduce the risk of back and other injuries occurring.
How do I learn to use the keyboard?
Typing is a physical activity and using a keyboard requires skill, hence the need to learn correct typing technique. Unskilled ('hunt and peck') typists are particularly at risk of OOS because they:
• often use only one or two fingers which may overload the finger tendons
• are constantly looking from keyboard to screen to keyboard, which may strain neck muscles
• often adopt a tense posture (wrists bent back and fingers 'poised to strike').
The most common way to learn to touch type is with a typing tutor.
One common commercial typing tutor is TYPEQUICK .
Alternatively you could use a search engine such as Google and search for a typing tutor.
Most organisations will have guidelines for typing accuracy and speed. They will also have guidelines for usage of computer equipment.